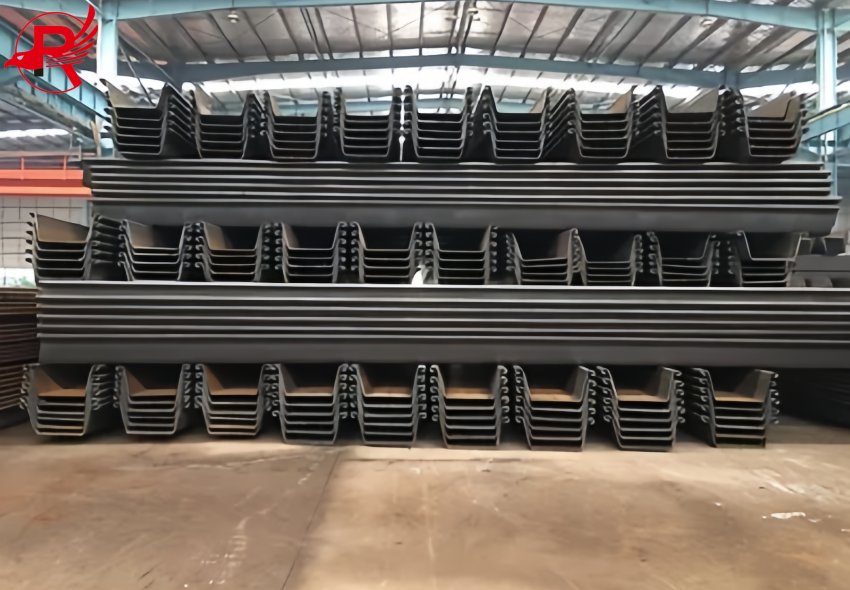
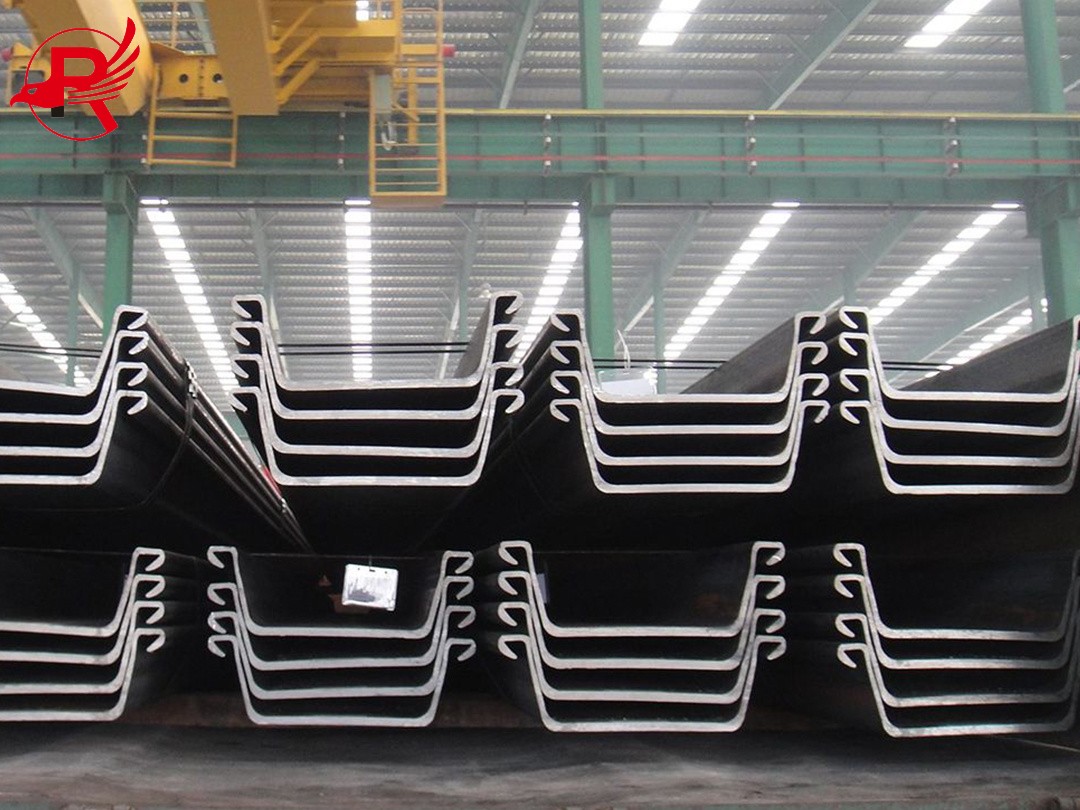
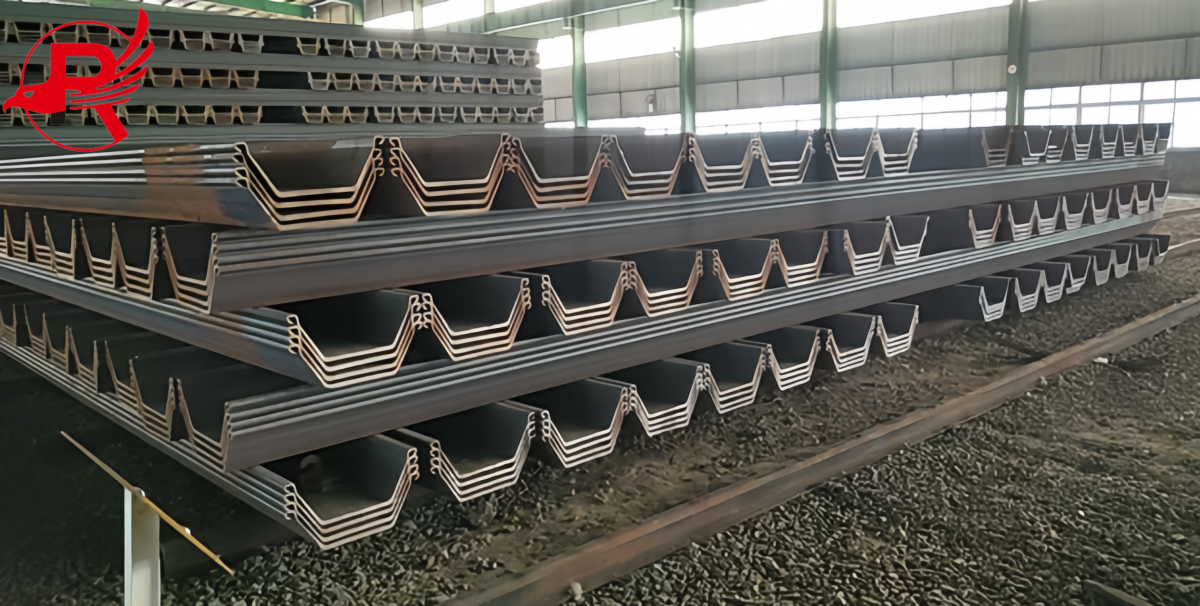
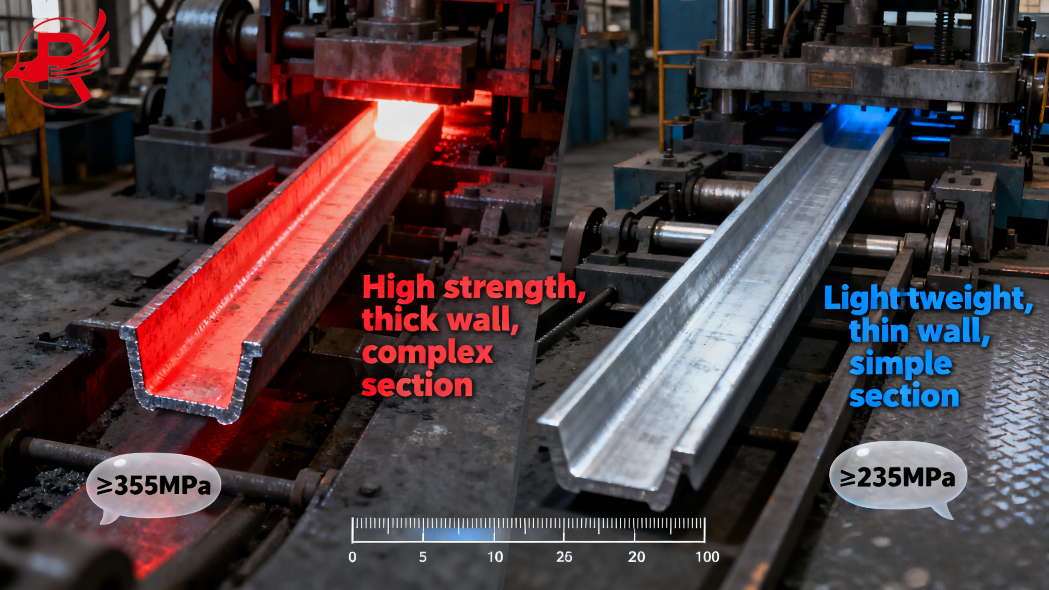
In the field of civil engineering and construction, Steel Sheet Piles (often referred to as sheet piling) have long been a cornerstone material for projects requiring reliable earth retention, water resistance, and structural support—from riverbank reinforcement and coastal protection to basement excavation and temporary construction barriers. However, not all Steel Sheet Piles are created equal: two primary manufacturing processes—hot rolling and cold forming—produce distinct products, Hot Rolled Steel Sheet Piles and Cold Formed Rolled Steel Sheet Piles, each with unique characteristics that make them suited for specific applications. Understanding their differences is critical for engineers, contractors, and project managers to make cost-effective, performance-driven decisions.



Address
Bl20, Shanghecheng, Shuangjie Street, Beichen District, Tianjin, China
Phone
+86 13652091506
Post time: Oct-03-2025
