Introduction to U Channel and C Channel
U Channel:
U-shaped steel, with a cross-section resembling the letter "U," complies with the national standard GB/T 4697-2008 (implemented in April 2009). It is primarily used in mine roadway support and tunnel support applications, and is a key material for the manufacture of retractable metal supports.
C Channel:
C-shaped steel is a type of steel formed by cold bending. Its cross-section is C-shaped, with high bending strength and torsional resistance. It is widely used in construction and industrial fields.
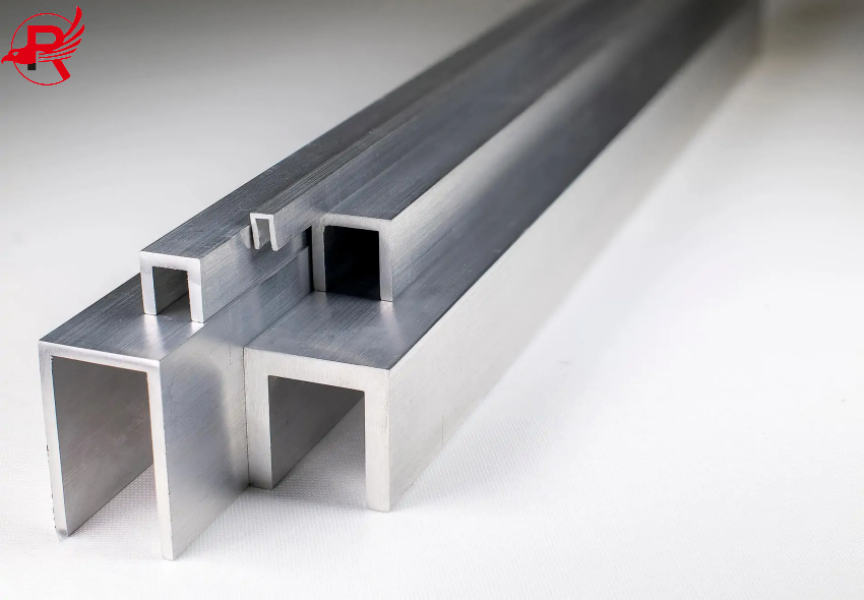



The difference between U-shaped steel and C-shaped steel
1. Differences in cross-sectional shapes
U Channel: The cross-section is in the shape of the English letter "U" and has no curling design. The cross-sectional shapes are divided into two types: waist positioning (18U, 25U) and ear positioning (29U and above).
C Channel: The cross-section is "C"-shaped, with an inner curling structure on the edge. This design makes it have stronger bending resistance in the direction perpendicular to the web.
2. Comparison of mechanical properties
(1): Load-bearing characteristics
U-shaped steel: The compressive resistance in the direction parallel to the bottom edge is outstanding, and the pressure can reach more than 400MPa. It is suitable for mine support scenarios that bear vertical loads for a long time.
C-shaped steel: The bending strength in the direction perpendicular to the web is 30%-40% higher than that of U-shaped steel, and is more suitable for bearing bending moments such as lateral wind loads.
(2): Material properties
U-shaped steel is produced using a hot-rolling process, with thicknesses generally ranging from 17-40mm, primarily made of 20MnK high-strength steel.
C-shaped steel is typically cold-formed, with wall thicknesses typically ranging from 1.6-3.0mm. This improves material utilization by 30% compared to traditional channel steel.
3. Application Areas
Main Uses of U-shaped steel:
Primary and secondary support in mine tunnels (accounting for approximately 75%).
Support structures for mountain tunnels.
Foundation components for building guardrails and sidings.
Typical Applications of C-shaped steel:
Mounting systems for photovoltaic power plants (especially ground-mounted power plants).
Purlins and wall beams in steel structures.
Beam-column assemblies for mechanical equipment.
Comparison of the advantages of U-shaped steel and C-shaped steel
Advantages of U-Shaped Steel
Strong load-bearing capacity: U-shaped cross-sections offer high bending and pressure resistance, making them suitable for applications requiring heavy loads, such as mine tunnel support and weighbridges.
High stability: U-shaped steel structures resist deformation and are less susceptible to significant wear and damage over long periods of use, providing superior safety.
Convenient processing: U-shaped steel can be flexibly fixed using pre-fabricated holes, allowing for flexible installation and adjustment, making it suitable for applications requiring frequent adjustments, such as rooftop photovoltaic mounting systems.
Advantages of C-shaped steel
Excellent flexural performance: The internal curled edge structure of C-shaped steel provides exceptional flexural strength perpendicular to the web, making it suitable for applications with strong winds or those requiring lateral load resistance (such as photovoltaic systems in mountainous areas or on coastal areas).
Strong connection: The flange and bolted connection design provides enhanced load-bearing capacity, making it suitable for complex structures or large spans (such as large factories and bridges).
Ventilation and light transmission: The wide spacing between beams makes it suitable for applications requiring ventilation or light transmission (such as platforms and corridors).
China Royal Steel Ltd
Address
Bl20, Shanghecheng, Shuangjie Street, Beichen District, Tianjin, China
Phone
+86 13652091506
Post time: Aug-08-2025
