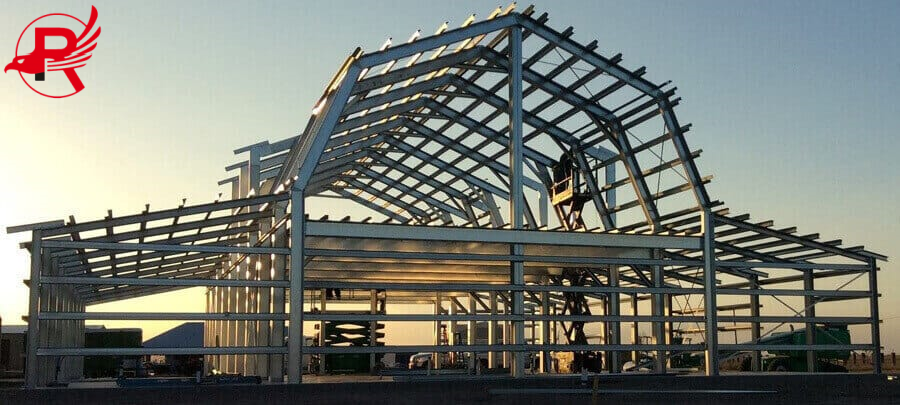

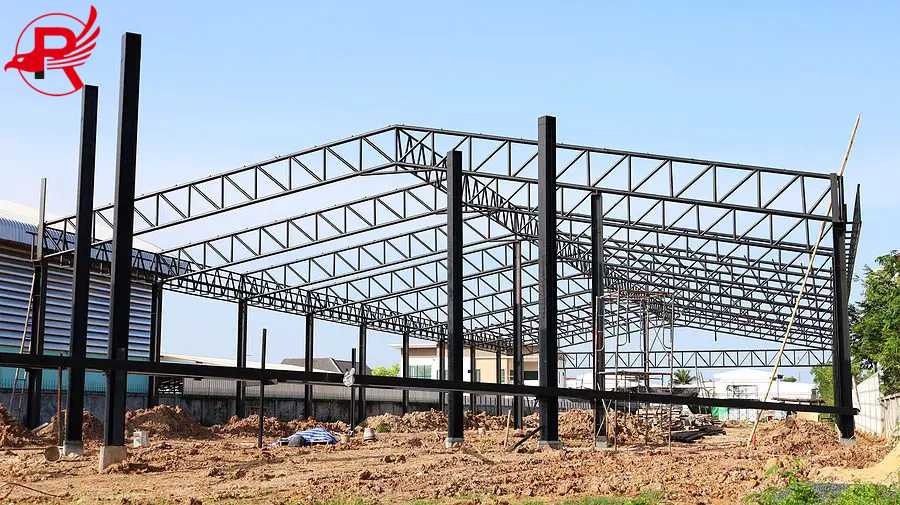
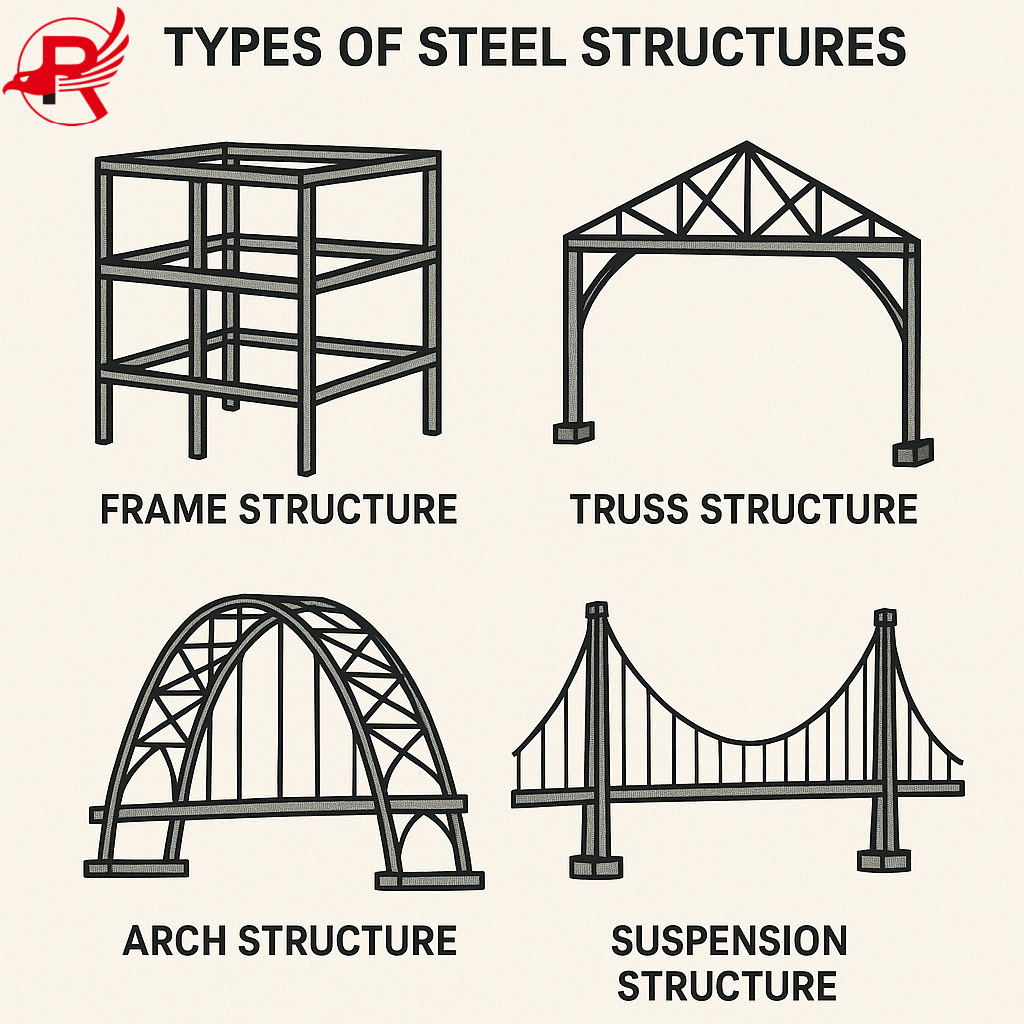
Steel structures building utilize steel as the primary load-bearing structure (such as beams, columns, and trusses), supplemented by non-load-bearing components such as concrete and wall materials. Steel's core advantages, such as high strength, lightweight, and recyclability, have made it a key technology in modern architecture, particularly for large-span, high-rise, and industrial buildings. Steel structures are widely used in stadiums, exhibition halls, skyscrapers, factories, bridges, and other applications.

Address
Bl20, Shanghecheng, Shuangjie Street, Beichen District, Tianjin, China
Phone
+86 13652091506
Post time: Oct-01-2025
