High Strength Structural Customized 6 inch 8 inch Hot Rolled Steel H Beam

PRODUCT PRODUCTION PROCESS
The production process of external standard H-shaped steel usually includes the following main steps:
Raw material preparation: The raw material for producing H-shaped steel is usually steel billet. The steel billet needs to be cleaned and heated for subsequent processing and forming.
Hot rolling processing: The preheated steel billet is sent to the hot rolling mill for processing. In the hot rolling mill, the steel billet is rolled by multiple rollers and gradually formed into the cross-sectional shape of H-shaped steel.
Cold working (optional): In some cases, in order to improve the accuracy and surface quality of H-shaped steel, the hot-rolled H-shaped steel will also be cold processed, such as cold rolling, drawing, etc.
Cutting and finishing: After rolling and cold working, H-shaped steel needs to be cut and finished according to the customer's requirements to meet specific size and length requirements.
Surface treatment: Clean and anti-rust treatment of H-shaped steel to ensure the surface quality and corrosion resistance of the product.
Inspection and packaging: Conduct quality inspection on the produced H-shaped steel, including inspection of appearance quality, dimensional accuracy, mechanical properties, etc. After passing the test, it will be packed and ready to be sent to the customer.

PRODUCT SIZE

| Designation | Unt Weight kg/m) |
Standard Secional imension mm |
Sectional Ama (cm² |
|||||
| W | H | B | 1 | 2 | r | A | ||
| HE28 | AA | 61.3 | 264.0 | 280.0 | 7.0 | 10.0 | 24.0 | 78.02 |
| A | 76.4 | 270.0 | 280.0 | 80 | 13.0 | 24.0 | 97.26 | |
| B | 103 | 280.0 | 280.0 | 10.5 | 18.0 | 24.0 | 131.4 | |
| M | 189 | 310.0 | 288.0 | 18.5 | 33.0 | 24.0 | 240.2 | |
| HE300 | AA | 69.8 | 283.0 | 300.0 | 7.5 | 10.5 | 27.0 | 88.91 |
| A | 88.3 | 200.0 | 300.0 | 85 | 14.0 | 27.0 | 112.5 | |
| B | 117 | 300.0 | 300.0 | 11.0 | 19.0 | 27.0 | 149.1 | |
| M | 238 | 340.0 | 310.0 | 21.0 | 39.0 | 27.0 | 303.1 | |
| HE320 | AA | 74.3 | 301.0 | 300.0 | 80 | 11.0 | 27.0 | 94.58 |
| A | 97.7 | 310.0 | 300.0 | 9.0 | 15.5 | 27.0 | 124.4 | |
| B | 127 | 320.0 | 300.0 | 11.5 | 20.5 | 27.0 | 161.3 | |
| M | 245 | 359.0 | 309.0 | 21.0 | 40.0 | 27.0 | 312.0 | |
| HE340 | AA | 78.9 | 320.0 | 300.0 | 85 | 11.5 | 27.0 | 100.5 |
| A | 105 | 330.0 | 300.0 | 9.5 | 16.5 | 27.0 | 133.5 | |
| B | 134 | 340.0 | 300.0 | 12.0 | 21.5 | 27.0 | 170.9 | |
| M | 248 | 377.0 | 309.0 | 21.0 | 40.0 | 27.0 | 315.8 | |
| HE360 | AA | 83.7 | 339.0 | 300.0 | 9.0 | t2.0 | 27.0 | 106.6 |
| A | 112 | 350.0 | 300.0 | 10.0 | 17.5 | 27.0 | 142.8 | |
| B | 142 | 360.0 | 300.0 | 12.5 | 22.5 | 27.0 | 180.6 | |
| M | 250 | 395.0 | 308.0 | 21.0 | 40.0 | 27.0 | 318.8 | |
| HE400 | AA | 92.4 | 3780 | 300.0 | 9.5 | 13.0 | 27.0 | 117.7 |
| A | 125 | 390.0 | 300.0 | 11.0 | 19.0 | 27.0 | 159.0 | |
| B | 155 | 400.0 | 300.0 | 13.5 | 24.0 | 27.0 | 197.8 | |
| M | 256 | 4320 | 307.0 | 21.0 | 40.0 | 27.0 | 325.8 | |
| HE450 | AA | 99.8 | 425.0 | 300.0 | 10.0 | 13.5 | 27.0 | 127.1 |
| A | 140 | 440.0 | 300.0 | 11.5 | 21.0 | 27.0 | 178.0 | |
| B | 171 | 450.0 | 300.0 | 14.0 | 26.0 | 27.0 | 218.0 | |
| M | 263 | 4780 | 307.0 | 21.0 | 40.0 | 27.0 | 335.4 | |
| Designatio | Unit Weight kg/m) |
Standad Sectional Dimersion (mm) |
Sectiona Area (cm²) |
|||||
| W | H | B | 1 | 2 | r | A | ||
| HE50 | AA | 107 | 472.0 | 300.0 | 10.5 | 14.0 | 27.0 | 136.9 |
| A | 155 | 490.0 | 300.0 | t2.0 | 23.0 | 27.0 | 197.5 | |
| B | 187 | 500.0 | 300.0 | 14.5 | 28.0 | 27.0 | 238.6 | |
| M | 270 | 524.0 | 306.0 | 21.0 | 40.0 | 27.0 | 344.3 | |
| HE550 | AA | t20 | 522.0 | 300.0 | 11.5 | 15.0 | 27.0 | 152.8 |
| A | 166 | 540.0 | 300.0 | t2.5 | 24.0 | 27.0 | 211.8 | |
| B | 199 | 550.0 | 300.0 | 15.0 | 29.0 | 27.0 | 254.1 | |
| M | 278 | 572.0 | 306.0 | 21.0 | 40.0 | 27.0 | 354.4 | |
| HE60 | AA | t29 | 571.0 | 300.0 | t2.0 | 15.5 | 27.0 | 164.1 |
| A | 178 | 500.0 | 300.0 | 13.0 | 25.0 | 27.0 | 226.5 | |
| B | 212 | 600.0 | 300.0 | 15.5 | 30.0 | 27.0 | 270.0 | |
| M | 286 | 620.0 | 305.0 | 21.0 | 40.0 | 27.0 | 363.7 | |
| HE650 | AA | 138 | 620.0 | 300.0 | t2.5 | 16.0 | 27.0 | 175.8 |
| A | 190 | 640.0 | 300.0 | t3.5 | 26.0 | 27.0 | 241.6 | |
| B | 225 | 660.0 | 300.0 | 16.0 | 31.0 | 27.0 | 286.3 | |
| M | 293 | 668.0 | 305.0 | 21.0 | 40.0 | 27.0 | 373.7 | |
| HE700 | AA | 150 | 670.0 | 300.0 | 13.0 | 17.0 | 27.0 | 190.9 |
| A | 204 | 600.0 | 300.0 | 14.5 | 27.0 | 27.0 | 260.5 | |
| B | 241 | 700.0 | 300.0 | 17.0 | 32.0 | 27.0 | 306.4 | |
| M | 301 | 716.0 | 304.0 | 21.0 | 40.0 | 27.0 | 383.0 | |
| HE800 | AA | 172 | 770.0 | 300.0 | 14.0 | 18.0 | 30.0 | 218.5 |
| A | 224 | 790.0 | 300.0 | 15.0 | 28.0 | 30.0 | 285.8 | |
| B | 262 | 800.0 | 300.0 | 17.5 | 33.0 | 30.0 | 334.2 | |
| M | 317 | 814.0 | 303.0 | 21.0 | 40.0 | 30.0 | 404.3 | |
| HE800 | AA | 198 | 870.0 | 300.0 | 15.0 | 20.0 | 30.0 | 252.2 |
| A | 252 | 800.0 | 300.0 | 16.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 320.5 | |
| B | 291 | 900.0 | 300.0 | 18.5 | 35.0 | 30.0 | 371.3 | |
| M | 333 | 910.0 | 302.0 | 21.0 | 40.0 | 30.0 | 423.6 | |
| HEB1000 | AA | 222 | 970.0 | 300.0 | 16.0 | 21.0 | 30.0 | 282.2 |
| A | 272 | 0.0 | 300.0 | 16.5 | 31.0 | 30.0 | 346.8 | |
| B | 314 | 1000.0 | 300.0 | 19.0 | 36.0 | 30.0 | 400.0 | |
| M | 349 | 1008 | 302.0 | 21.0 | 40.0 | 30.0 | 444.2 | |
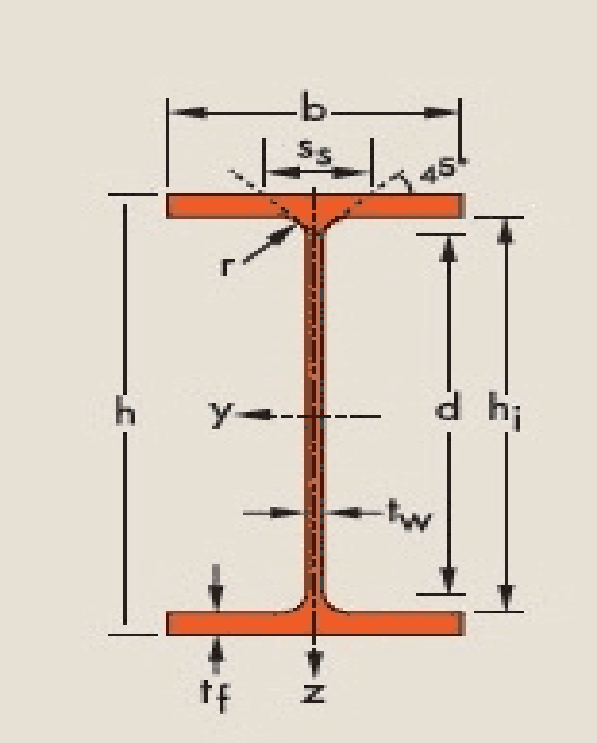
EN H-Shaped Steel
Grade: EN10034:1997 EN10163-3:2004
Specification:HEA HEB and HEM
Standard: EN
FEATURES
1. Excellent Mechanical Properties
Strong Flexural Resistance: Wide and thick flanges with a large cross-sectional moment of inertia (Ix) significantly outperform I-beams (30%-50% higher at the same weight).
Excellent Compressive Stability: The flanges are perpendicular to the web, resulting in a high local buckling critical stress, making them suitable for column support.
Balanced Biaxial Stiffness: X- and Y-axis moments of inertia are similar (e.g., HM type), resulting in excellent lateral force resistance.
2. Lightweight and Economical
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: 15%-20% lighter than ordinary I-beams for the same load-bearing capacity (reducing structural loads and foundation costs).
Material Savings: High cross-sectional efficiency reduces steel usage (e.g., for a 30-meter span factory building, H-beams use 40% less steel than concrete beams).
3. Convenient and Efficient Construction
Easy Bolting: The flat flange surface facilitates high-strength bolting.
Reduced Welding: Standardized components are prefabricated in the factory, enabling faster on-site assembly (reducing construction time by 30%).
4. Highly Standardized Cross-Sectional Specifications
National Standard (GB/T 11263): HW (wide flange), HM (medium flange), and HN (narrow flange) series, covering sizes from 100×100 to 1000×300 mm.
American Standard (ASTM A36): The W series (e.g., W12×30) is universally accepted.
PRODUCT INSPECTION
The requirements for H-shaped steel inspection mainly include the following aspects:
Surface Defects
Not permitted:
Cracks, scars, or folds greater than 0.3mm in depth;
Rust pits that affect strength (depth greater than 5% of wall thickness);
Zinc coating detachment (for corrosion-resistant models).
Minor defects permitted:
Local scratches ≤ 0.2mm in depth;
Pockmark area ≤ 1cm²/m².

PRODUCT APPLICATION
External standard H-beams are widely used in the construction and engineering fields, including but not limited to the following aspects:
Structural engineering, bridge engineering, machinery manufacturing, shipbuilding, steel structure construction,

PACKAGING AND SHIPPING
Packaging and transportation of external standard H-beams usually require following the following steps:
Packaging: H-shaped steel is usually packaged according to customer requirements to protect its surface from damage. Common packaging methods include bare packaging, wooden pallet packaging, plastic packaging, etc. When packaging, it is necessary to ensure that the surface of the H-shaped steel is not scratched or corroded.
Labeling: Mark clear product information on the packaging, such as model, specification, quantity, etc., to facilitate identification and management.
Loading: When loading and transporting the packaged H-shaped steel, it is necessary to ensure that there will be no collision or extrusion during the loading process to avoid product damage.
Transportation: Choose appropriate transportation tools, such as trucks, railway transportation, etc., and choose the appropriate transportation method according to customer requirements and transportation distance.
Unloading: After arriving at the destination, unloading operation needs to be done carefully to avoid damage to the H-shaped steel.
Storage: Store H-shaped steel in a dry and ventilated warehouse to avoid moisture or other adverse effects.


COMPANY STRENGTH
FAQ
1.How can I get a quotation from you ?
You can leave us message, and we will reply every message in time.
2.Will you delivery the goods on time?
Yes,we promise to provide best quality products and delivery on time. Honesty is our company's tenet.
3.Can I get samples before order ?
Yes, of course. Usually our samples are free,we can produce by your samples or technical drawings.
4.What is your payment terms?
Our usual payment term is 30% deposit, and rest against B/L. EXW, FOB,CFR, CIF.
5.Do you accept the third party inspection?
Yes absolutely we accept.
6.How do we trust your company?
We specialise in steel business for years as golden supplier, headquarter locates in Tianjin province, welcome to investigate in any ways, by all means.










